This is the definitive guide on how to get found in Google search fast. I’m going to show you the 20 steps to follow to make your website not only visible on Google but rank as high as possible in the search results.
Let’s get started.
- Verify your website with Google Search Console
- Submit a Sitemap to Google
- Check for Google Penalties
- Make sure your website is Mobile Friendly
- Make sure your website is HTTPS
- Check your canonical URLs
- Make your website load as fast as possible
- Optimize your site structure
- Add an ALT text to all images
- Enable breadcrumb lists
- Optimize your page titles
- Write meta descriptions for all pages
- Revise your page headings
- Add structured data markup
- Optimize your content for the Google featured snippet
- Publish high quality relevant content
- Target long tail keywords
- Guest Post on other websites
- Boost your posts on Facebook
- Promote your brand online
Step 1: Verify your website with Google Search Console
While Google is doing a great job in finding new websites and content, you can help them discover new content faster, through the Google search console.
The Google search console is a set of free tools and reports provided by Google to webmasters to help them improve their website’s performance on Google search.
The first step to getting started with Google search console is to add and verify your website.
Then you should check for crawl errors to make sure that Google can crawl and index your pages without any problems.
Step 2: Submit a sitemap to Google
A sitemap is a file in the root folder of your website that lists all URLs (permalinks) that search engines need to know about.
Although a sitemap does not directly influence your rankings, it helps Google during the crawling and indexing phase.
You can use a sitemap to tell Google which URLs to index and when each page was updated.
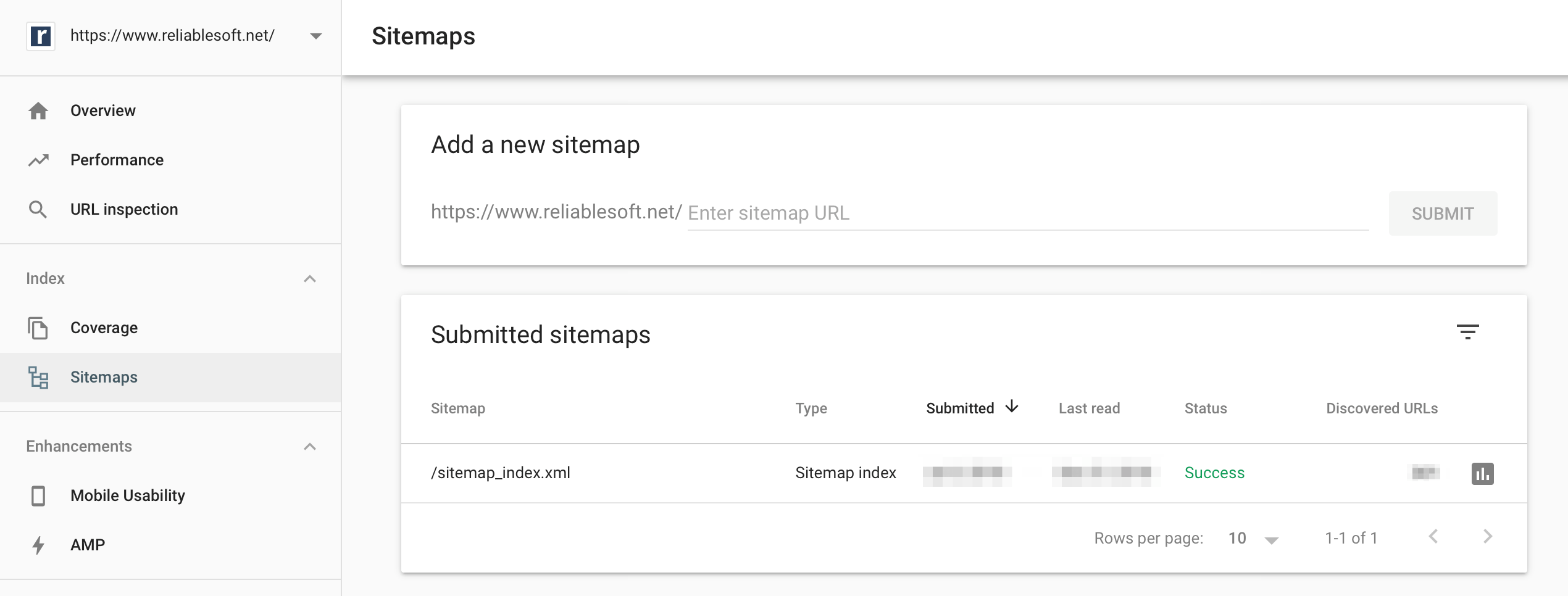
The first step is to create and optimize your sitemap for SEO and the second step to submit sitemap to Google using one of the three available methods.
Step 3: Check for Google Penalties
For a website to get found on Google, it has to be free of Google Penalties.
Google may impose either a manual or algorithmic penalty to a website if it finds that it violates any of the Google webmaster guidelines.
For example, if you try to manipulate the Google ranking algorithms by purchasing links from low-quality sites with the purpose of improving your Google search position, sooner or later Google will find out about it and remove your website from their index.
So, before proceeding with the next steps, follow the instructions here to check if your website is penalized by Google and take the necessary steps to recover from any penalty.
Step 4: Make sure your website is Mobile Friendly
If you want to rank higher on Google, your website has to be mobile-friendly.
The majority of Google searches are now performed on mobile devices and with the introduction of Google’s mobile-first index, you really have no choice but to optimize your website for mobile.
The first step is to run the Google mobile-friendly test and make sure that there are no issues. This means that your website is mobile-friendly, but that’s not the end of the story.
You need to take it a step further and optimize your content for mobile. This means adjusting your meta description length to make your search snippets mobile-friendly, optimizing your images and removing design elements that are not suitable for mobile devices.
Review your Google analytics device reports and try to improve your website’s performance on mobile by analyzing different metrics like time on spend on a page, bounce rate and exit pages.
Step 5: Make sure your website is HTTPS
Having an SSL installed on your website is a known ranking factor. Google rewards secure websites by increasing their visibility in the search results.
In addition, websites with HTTPS are trusted by users and this has a number of other benefits.
If you don’t have an SSL installed yet, add this on top of your list. You can read this guide on how to migrate to https without negatively affecting your SEO.
Step 6: Check your canonical URLs
A website domain can start with www or no www. For example https://www.reliablesoft.net or https://reliablesoft.net.
While this is the same website, in the eyes of Google, these are considered two different websites. If you also consider the non-https URLs, then for a single domain, you can have four different variations.
If you don’t tell Google which is your preference, it might get confused. The way to do this is by setting the canonical link element.
This is how it looks like in HTML code:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.reliablesoft.net/get-found-on-google" />
This is an HTML tag that is added to all your website pages that specify the preferred version.
For example, if you have set up your CMS to respond to URLs starting with “https://www” then the canonical URLs on your pages should reflect this.
The canonical URL is important for many other uses, it helps to eliminate duplicate content issues and consolidating incoming links to a specified URL.
You can read this guide to get started with canonical URLS.
Step 7: Make your website load as fast as possible
Google and users want websites that load fast. Nobody likes to wait for a long time for a page to load and that’s why Google added loading speed as a ranking factor.
If you want to get your website to the first page of Google, it has to load as fast as possible.
Google considers a website fast when it loads in less than 3 seconds on mobile.
That’s not easy to achieve, and you may have to get help from an experienced web developer to get to those numbers but it definitely worth the effort.
Start by analyzing your website’s performance using the Page Speed Insights tool and also the Google Mobile Speed Test.
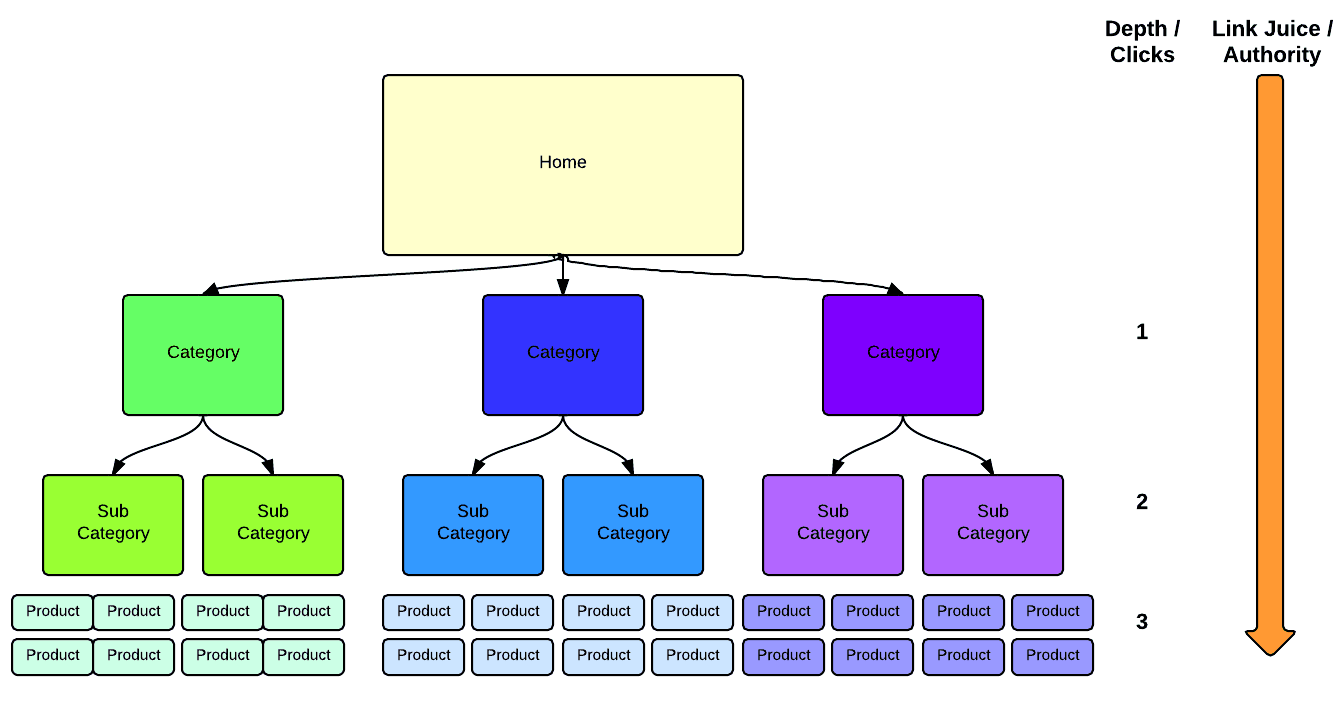
Step 8: Optimize your site structure
The structure of your website is very important for rankings. From my experience, this is an element that a lot of webmasters ignore. Instead, they concentrate on the visual aspect of a website and forget about optimizing their site structure.
A good site structure has the following characteristics:
- It has a hierarchical format (see diagram below)
- Every page on your website is accessible from the homepage in less than 3 clicks
- It has a simple navigation menu and SEO friendly URLs
- Content is grouped into logical categories
Step 9: Add an ALT text to all images
A typical website has a lot of images. Images are needed to make reading easier and to present a product or idea in a visually appealing way.
To increase your chances of appearing on Google image search and to make your images accessible by Google you need to ensure that you provide an alt text for all images.
The alt text is a text that describes an image and is added to the ALT HTML tag. Here is an example:

By optimizing your images for SEO, you also increase your chances of getting found for related searches on Google web search.
Step 10: Enable breadcrumb lists
Another way to make your navigation structure friendlier to users and Google is to make use of breadcrumb lists.
A breadcrumb trail is a small menu appearing on the top of each page that helps users navigate to a previous step (until they reach the home page).
Google is using the breadcrumb menu in the search results and also for understanding your site structure better.
Here is an example of a breadcrumb menu:

Step 11: Optimize your page titles
Page title optimization is perhaps the most important SEO element. This is one of the SEO factors that hasn’t changed since the beginning of Google.
A good page title accurately describes the page’s content using language that is related to what the users are searching on Google.
When users browse the search results, they are most likely to click to the title is a closer match to the search terms they have used.
So, before proceeding any further review your page titles for all your website pages and make sure that:
- Each and every page on your site has a unique title
- The length of your title is no more than 80 characters
- The titles include keywords that both Google and users can recognize
Don’t omit this step. Allocate the necessary time on this task as it can help your pages to be found on Google for various keywords.
Here is an example of an SEO optimized page title:

Step 12: Write meta descriptions for all pages
Another important element of on-page SEO optimization is the meta description tag.
The meta description is shown as a search snippet in the Google results and it is your chance to advertise your page to Google users.
Follow these best practices:
- Add a unique meta description tag to all your pages
- In your description blend keywords and text that describes the page content
- Don’t repeat the title in the meta description
- Avoid using automated or generic descriptions
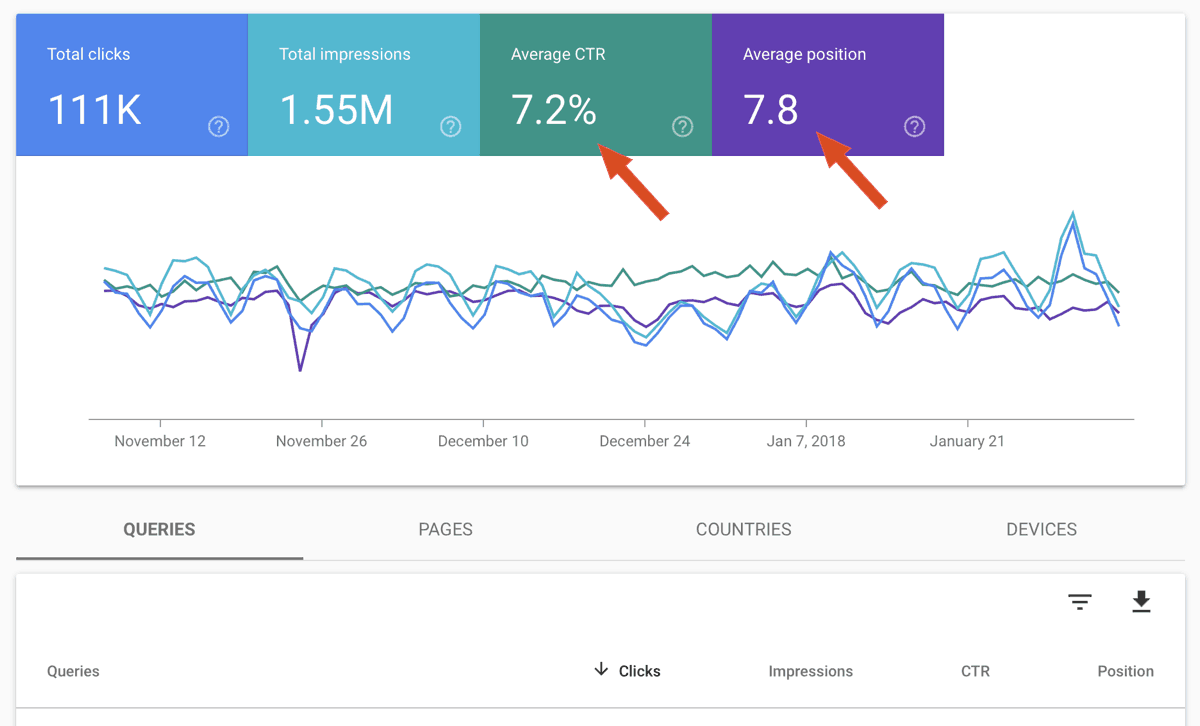
Review the performance report in Google search console to find pages that rank on the first page of Google but have a low CTR (Click Through Rate) and optimize your meta descriptions to attract more clicks.
Step 13: Revise your page headings
Another element that can help Google understand your content better is page headings.
Besides the page title, a webpage can have several headings. For best practices, these should be organized in a hierarchical structure.

In a typical scenario, the title of the page is the H1 tag and the rest of the headings used in the content, are H2 and H3.
Headings can make long-form content easier to read, especially for users who do skim reading.
Take for example this post, the H1 Tag is “How to get found on Google”, which is also the same as the page title, and the different steps are H2 tags.
Step 14: Add structured data markup
Schema markup and structured data is a modern way to describe parts of your data to search engine crawlers.
To make their life easier, all major search engines have agreed to set common rules that webmasters can follow to help them understand the context of the content.
For example, if you have a page selling an online SEO Course, you can use the product schema to tell search engines what is the title, description, and price of your product.
The way to ‘tell’ search engines is by adding pieces of code into your HTML, known as structured data.
You can learn more about how Google users structured by visiting the Google Search Gallery.
Step 15: Optimize your content for the Google featured snippet
By adding structured data to your pages, you increase your chances of appearing in a Google featured snippet.
A Google featured snippet is shown on top of the results and this translates to a higher CTR and more traffic to those websites.
Here is an example of a Google featured snippet when you search for “Become an SEO Expert” on Google.

To optimize your content for Google’s featured snippet you need to structure your content is such a way as to help Google pick up pieces of it and show it as a featured snippet.
You can read all the details in my previous guide: How to get a Google featured snippet
Step 16: Publish high-quality relevant content
So far, all the steps described above have to do with technical and on-page SEO. Another critical step is getting more visibility in Google search results, it’s the quality of your content.
What is high-quality content? If you search Google for this, you’ll get different opinions and you might get confused.
To simplify things, follow the rules below:
Do your keyword research
Publish content that is relevant to what the user is searching for. Do your keyword research and find out what keywords people type in the search box and create content that answers their question.
Target one topic per page
Try to target a single topic/keyword per page. Mixing up many keywords in a page for the purpose of targeting more keywords in a single post, is not the way to go.
Google was to show the most relevant content for a search query so keep to the point and avoid confusing Google by adding content to a page, that is not closely relevant to what the user is searching for.
Make your posts long enough but no need to exaggerate
Make your posts long enough and informative but have in mind that Google does not rank a page based on the length of the content but on relevancy. So, if you can fully cover a topic or answer a question in 800 words, then no need to make your content longer.
There is a lot of research that shows that long-form content performs better in search but this is provided that the content is highly relevant to the target keyword.
Expertise – Authority – Trustworthiness (EAT)
For all content published on your website, you need to prove to Google about your expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (EAT).
This means adding an author to all pages, creating an about us page that describes your expertise and getting links from high trusted and related websites that prove your authority about a subject.
You can review the Google Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines to get a better idea of how Google perceives the authority and trustworthiness of the content.
Step 17: Target long-tail keywords
Everybody wants to be found on Google for high volume keywords. Achieving top rankings for keywords that have a lot of monthly searches can make a huge difference for a website.
The problem is, high volume keywords are also highly competitive. In simple words, this means that it is practically impossible for a new website or a small business website to get on top of Google for those terms.
When you realize this, it can be disappointing at first but there is a way out long-tail keywords.
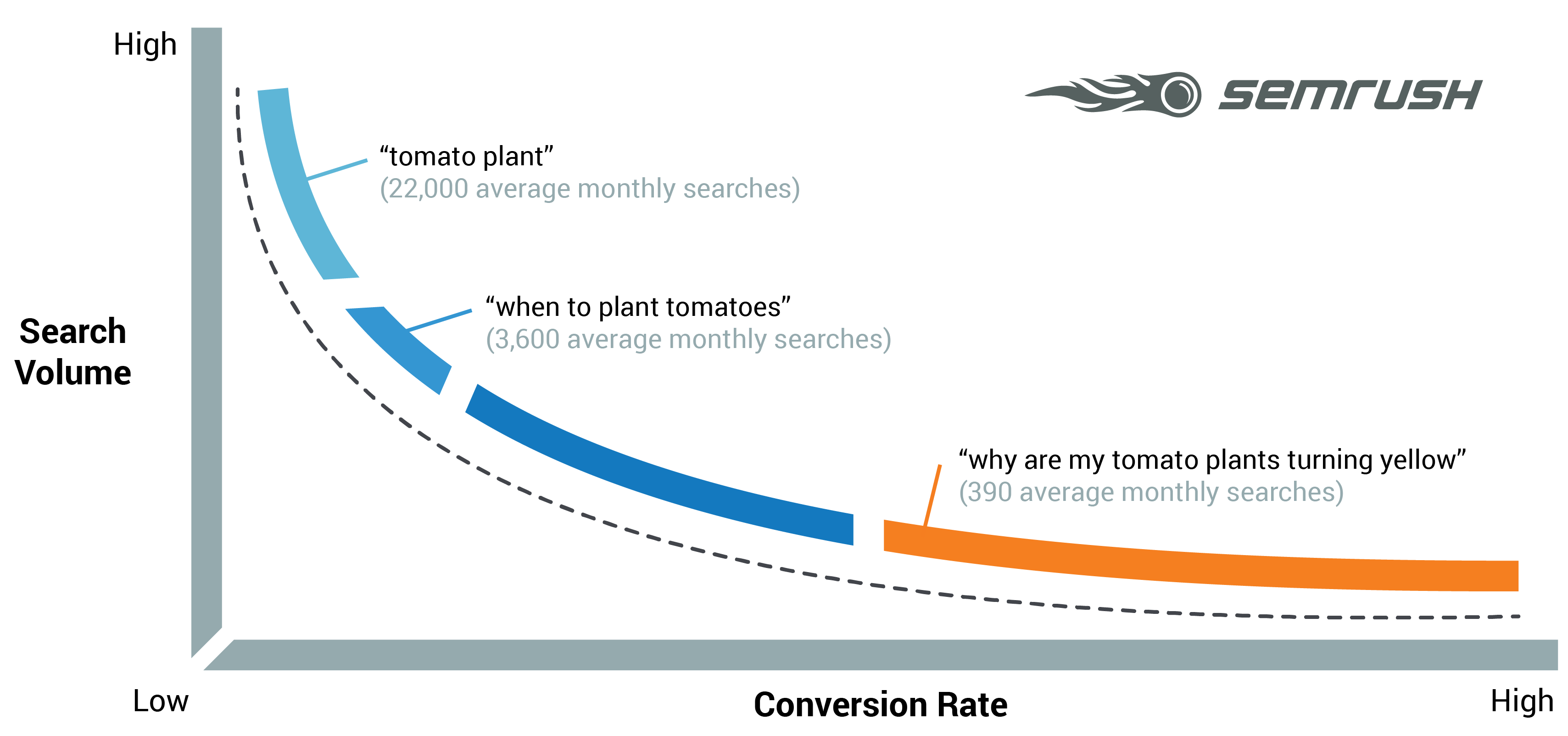
Long tail keywords are keywords that have less search volume and less competition compared to head keywords. They are search queries made up of two or more keywords.
Here is an example of a high volume head keyword: “SEO”
Here is an example of a long-tail keyword: “SEO Tutorial for Beginners”
The good news is that:
- it’s feasible to rank high for long tail keywords
- Long tail keywords make up 70% of Google searches
- Every day there are thousands of long tail keywords searched in Google for the first time.
The main takeaway is that you need to adjust your content marketing strategy and target keywords that you can actually rank for.
Step 18: Guest Post on other websites
The last three steps have to do with Off-Page SEO. Off-page SEO is all about website promotion and one of the ways to promote your website and get backlinks is through guest posting.
If you are not familiar with guest posting, this is how it works:
- You find websites that are related to your niche and have high Google rankings and authority.
- You contact them offering them content that is useful for their audience.
- Below the content (usually in the author bio) or within the body of the content (recommended), you add links pointing to your website.
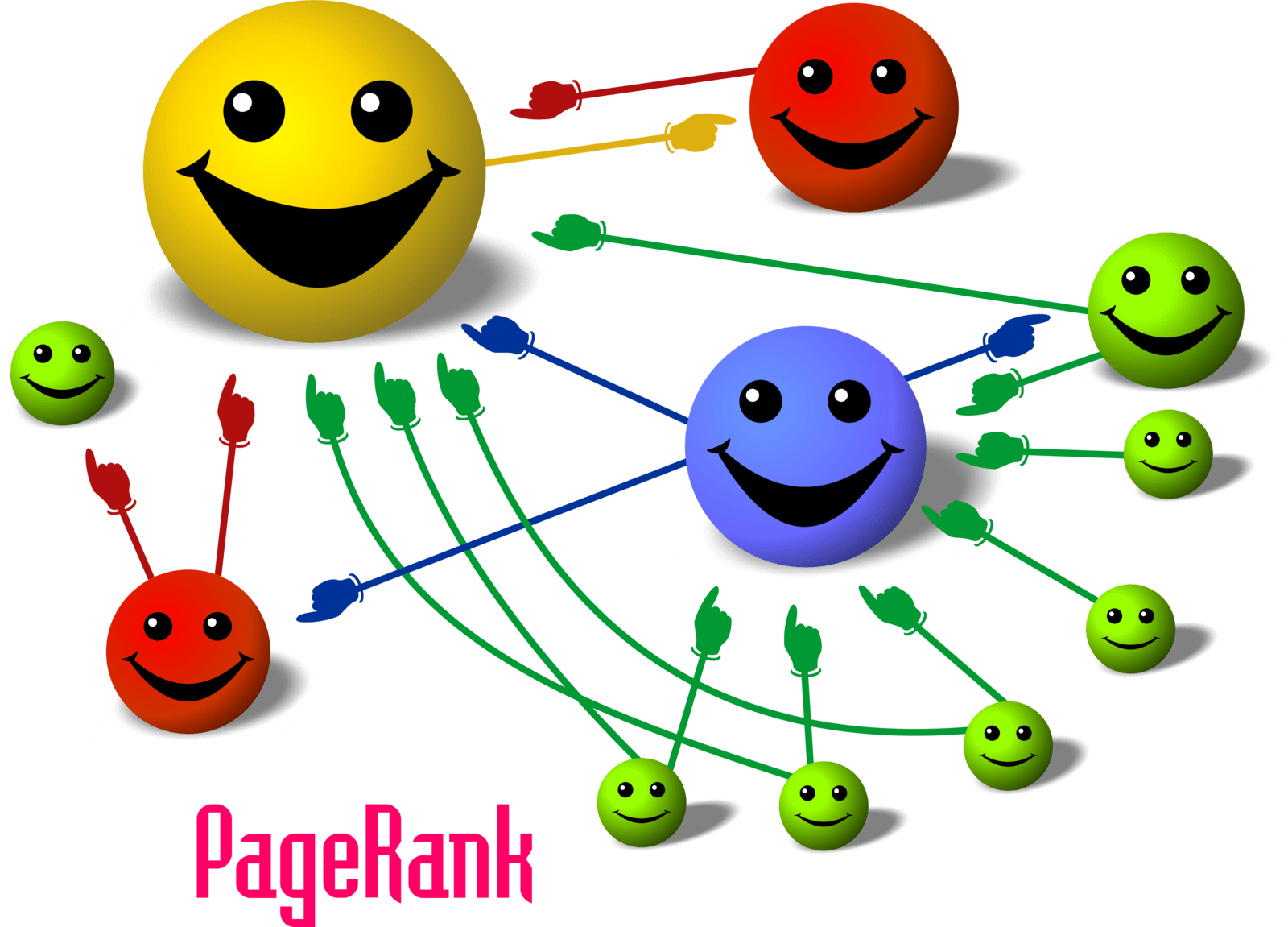
- When the post is published, Google finds the links and considers them as ‘votes of trust’.
- This will eventually increase your PageRank and your Google rankings will be improved.
This is a simplified description of how guest posting works, which is one of the forms of link building.
Look at the diagram below to understand the importance of links in rankings:
Step 19: Boost your posts on Facebook
Another way to promote your website and get it in front of more eyes is through Facebook.
If you don’t have a Facebook Business page yet, go to Facebook and create one. Then add on FB every post published on your website and use the ‘Boost Post’ feature to promote your posts to a custom audience.
Promoting your Facebook posts can help improve your visibility on Google.
Here is why:
- More people will see your posts and this increases the chances of getting natural links, which in turn will improve your Google rankings.
- More people will get to know your brand and start searching for it on Google. Brand searches can positively influence rankings.
- Your posts will get more likes and exposure on Facebook, which is always a good thing.
- It’s a way to get more traffic to your website and increase the number of repeating visitors.
Read this guide to get started: How to increase website traffic using social media
Step 20: Promote your brand online
Last but not least, one of the factors that play a huge role in what positions your content is found on Google for related searches is branding.
Google loves brands and they want to show in their search results brands that people like.
So, besides the typical SEO factors (content, incoming links, etc.), they (Google), scan the web to find out what people think of a brand.
If a brand is discussed heavily in forums, social networks and other channels (like YouTube), then it is more likely that it will do well on Google search than a brand that has no mentions at all.
As part of your digital marketing strategy, you should encourage any form of promoting your brand online and getting mentions (either in the form of links or just mentions of your brand), from other reputable sites on the Internet.
Although this step is indirectly related to Google rankings, I added it to stress the fact that you need to need to start thinking of ways to promote your website beyond Google. Doing that successfully will ‘force’ Google to follow the trend and ‘re-think’ of how it treats your website on Google search.
Key Learnings
You don’t have to be an SEO specialist to get your website found on Google. If you follow the 20 steps outlined above, it is certain that your Google rankings will start improving and this will eventually translate to more Google traffic.
One thing to have in mind is that it takes time for SEO related changes to work and for a website to be found on the first page of Google.
Even if you do everything correctly, it may take up to 6 months for a new website to get traffic from Google so be patient.
Go through the steps one by one and make sure that everything is handled properly (especially the technical and on-page SEO factors) and then concentrate on publishing high-quality relevant content and on promoting your brand in the best way possible.
What else is missing from the list that is critical in getting a website on Google, as fast as possible? Let me know in the comments below.





Leave a Reply