Once you get started with on-page SEO, the first task in your list is title tag optimization. Title tags are very important for SEO for two main reasons.
First, the title tag is shown in the search results so this is what users see even before visiting your website and second, it gives a big hint to search engines on what the page is all about.
This combination makes optimizing the title tags, a crucial step in the whole SEO process.
In this post, you will learn what is an HTML post title tag, what is the difference between a title tag and the page heading, how to write good title tags before publication, and how to optimize your title tags after publication (this is a must-read section).
What is the title tag?
Each page or post published on the Internet has an HTML title tag <title></title> defined in the <head></head> of the page.
If you are using any modern CMS like WordPress, the title tag is created automatically based on what is written in the title of a page or post.
So, in essence, the HTML title tag is the “official” title of a page. This is what will be shown in the SERPs (search engine results pages) but it is not necessary the same as what users will see when visiting your page (that’s the heading of the page – more on this below).
The title tag is also used as the title of a page or post when shared in social media. For example, when you paste a link on Facebook, the snippet will show the title of the page, among other things.
How to find out what is the title of a page?
There are 2 easy ways to check what is the value of a <title> tag for any page or post.
- Open a new browser window and navigate to the page URL. Right-click with your mouse anywhere on the page and select VIEW SOURCE. Search for <title>.
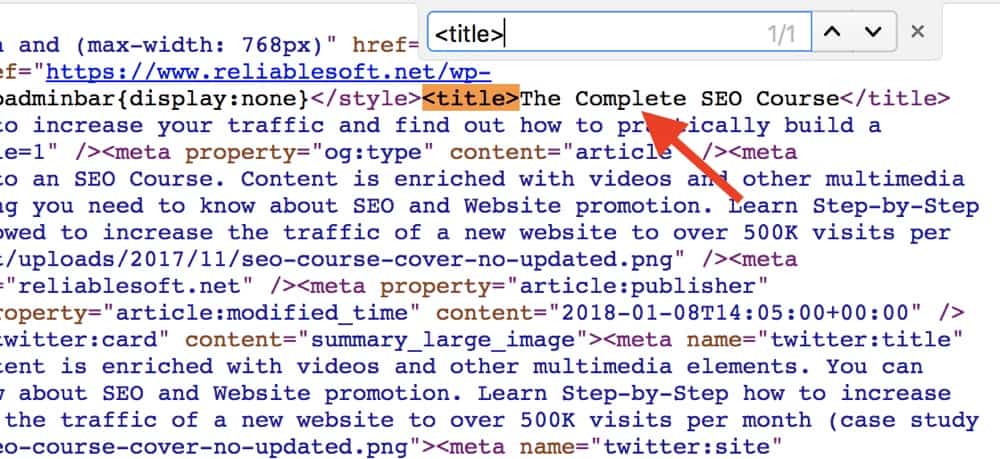
Whatever is enclosed in <title></title> is the page title.
- A faster way to view the page title is to move your mouse over the browser tab window.
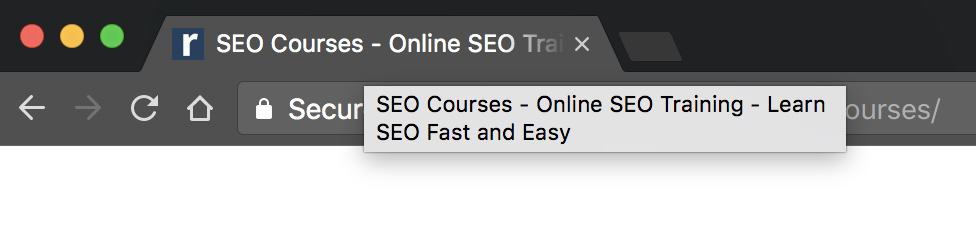
Browsers like Chrome, Safari, and Firefox will show you the page title. Here is an example of how the title for our SEO Courses is shown in the browser tab.
What is the difference between a title tag and page heading?
Before proceeding to the optimization step and how you can write good titles, it is necessary to understand the difference between the page title tag and the page H1 heading.
As mentioned above, platforms like WordPress create the title tag automatically from whatever you write as a page or post title in the WordPress editor.
Once you hit publish, both have the same value but in the background, these are two different things.
Have a look at the two examples below:
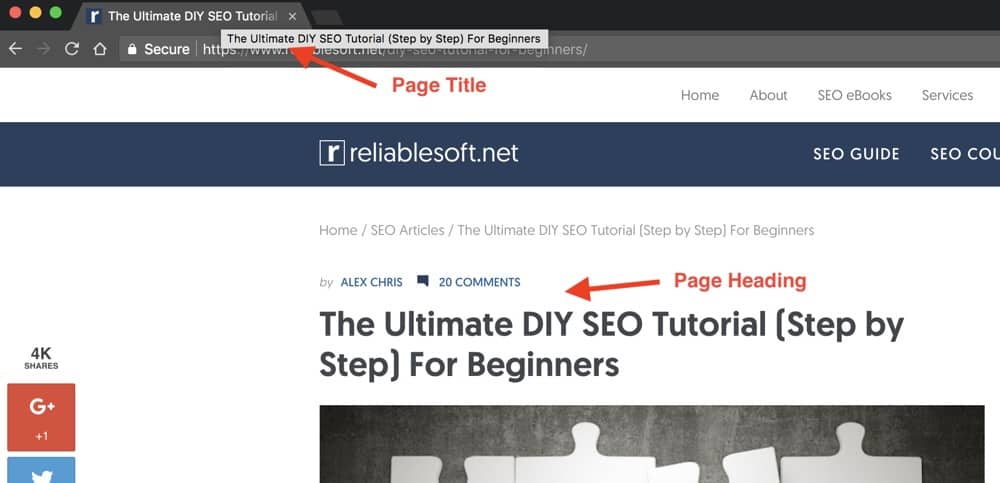
In the example above both the page title and page heading are the same while in the example below the page title has a different value than the page heading.
In other words, these two don’t have to be the same. As we will see below, you can customize your page title to be different than the page heading (H1).
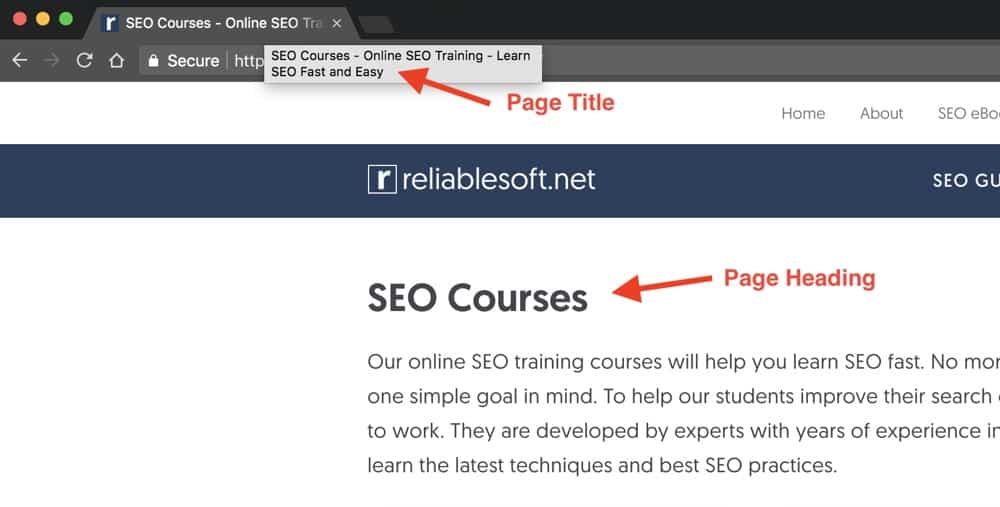
How can you make the title tag different from the page heading?
The most popular way is to install Yoast SEO plugin. Once activated on your WordPress website, Yoast SEO will add an extra box below each post that allows you to customize the page title.
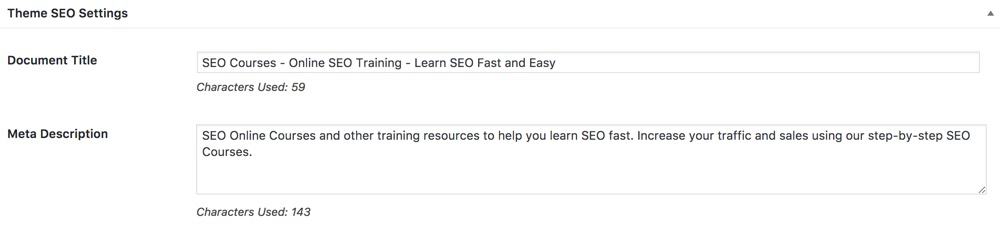
If you don’t want to use the Yoast SEO Plugin, you can make use of the Document Title or SEO Titles areas provided by your theme like the example below from a Genesis Framework WordPress Theme.
Genesis is my favorite WordPress theme and framework and the one I use for all my websites.
Should the title tag and page heading be the same or different?
One of the most popular questions many beginners to Search Engine Optimization ask me, is whether they should make the title tag and page heading the same.
The answer is simple. 90% of the cases both have the same values because most CMS and website tools are configured this way and this is perfectly fine.
So, there is nothing wrong with having the same value. This is also how all my posts are configured in the beginning.
Later, as part of the ongoing on-page SEO process or during an SEO audit (which is one of the digital marketing services we offer), I may go back and optimize the page title and differentiate it from the page heading.
I will explain below the process in more detail and show you how you can increase your traffic by making simple tweaks to your page titles.
What you should understand now is that there are no SEO issues if both the page title and page heading have the same value.
How to create good search engine friendly title tags?
Now that you know what is a title tag and how it differs from the page heading H1 tag, let’s see how to craft page titles that are SEO and user friendly.
Best Practices
Each and every page of your website should have a unique title tag
Each page (and that includes your homepage and posts), should have a unique title. This helps search engines understand how the particular page is distinct from other pages on your website.
Remember that one of the most complicated tasks search engine crawlers have to perform during the indexing process, is to understand the content and context of a page, and the page title is a great way to help them in that manner.
Note: If you are running an eCommerce website, read my post on homepage SEO for more tips on how to optimize the home page title of an eCommerce website.
A page title should accurately describe the page content
Think of the title as a very short summary of the page. A good title is highly relevant to the page content. Don’t try to trick search engines by providing for a title that is not supported by the content.
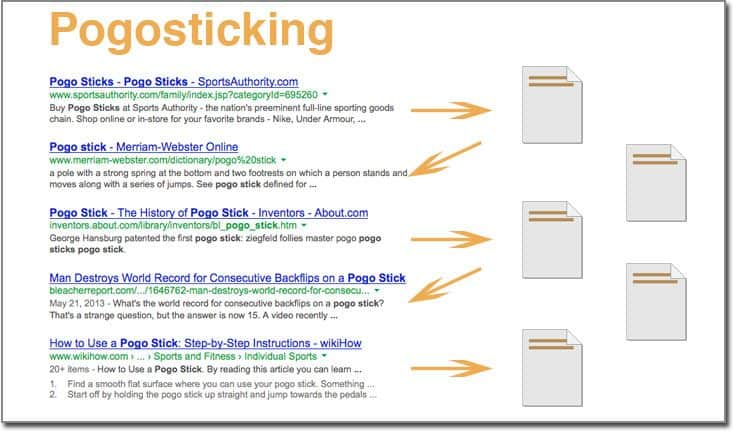
This is a bad SEO practice that can literally destroy your rankings because of what is called pogo-sticking.
Pogo sticking is the term used to describe the process where a user is searching something on Google, clicks on one of the top results, visits a page but doesn’t find it interesting and goes back to the search results and clicks on the second listing, etc.
Google can identify this user behavior and pattern and if a lot of users are doing the same thing then it means that they are not satisfied with the Google search results.
Google algorithms will then push the rankings of the particular pages down and show other pages to users until pogo-sticking is reduced, which is an indication that users are happy with the listed results.
Titles should be brief and informative (typically less than 60 characters)
The common guideline for the title length is between 50-60 characters. Most SEO experts and tools use this guideline because this is on average the number of characters that are shown in Google search results for the title of a snippet.
So, one of the reasons you should prefer short titles over longer ones is to ensure that your title will be shown without breaks in the SERPS, providing a better user experience and a higher CTR.
Titles should include your target keywords (but no keyword stuffing)
This is extremely important. A well-crafted title should include your target keyword. This is not against any Google guidelines, on the contrary, this is a good SEO practice.
A good title helps both search engines and users understand what the page is about, and having your keywords in the title is a step towards that direction.
We will see below some examples of how to do this without exaggerations. Keyword stuffing (i.e. repeating variations of the same keyword) in the title (and your content in general), should be avoided.
Create titles for users and not search engines
This is also very important. Your titles should be interesting enough to catch the attention of the users.
Here are some easy guidelines to follow to create catchy titles that are both SEO friendly and user friendly.
- Use Emotional Words in your titles
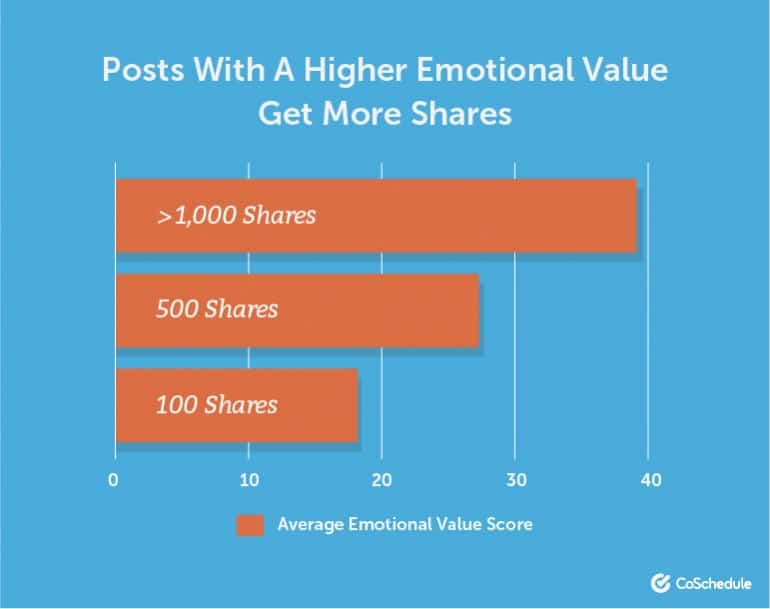
In a study by Co-schedule they found out that posts with emotional headlines get more shares.
This is strongly related to post titles since in the majority of cases people tend to share a post because of the title only. The fact that they actually went on to share it, it means that it caught their attention.
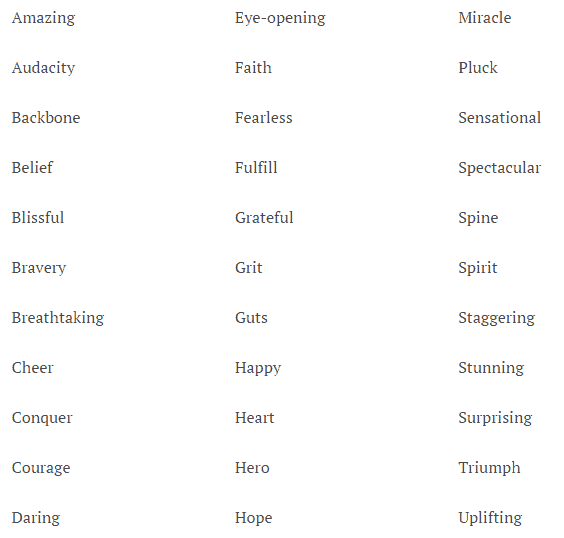
Here is a list of power words you can use in your titles, as explained in a previous post: How to write SEO friendly blog posts.
- Add Brackets to the end of your titles
This is another technique I’m using that is also backed by research.
As explained by Brian Dean in his article on RankBrain, titles with brackets have a 33% higher CTR than post titles without brackets. The study was performed by HubSpot and Outbrain after analyzing more than 3M headlines.

Here are a few examples of my titles with brackets that perform really well.

Should you add the domain to the title?
That’s another popular question. The answer is both yes and no.
Include your domain in the title:
- For your homepage title
- When you have a strong brand name, put your brand in the title first
If you don’t have a strong brand name you can add your domain at the end of the title or omit it since Google will add it automatically at the end of your post title in the search results.
In the example below my post title is “How to Successfully SEO Ecommerce Product Pages” but in the Google search results, it appears with my domain name appended at the end.
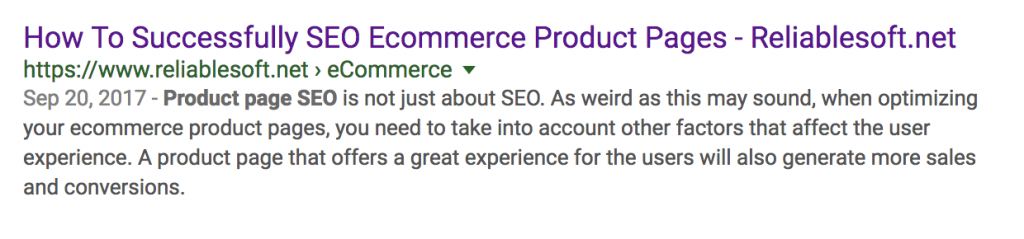
Optimize your URLs based on the title
Although this is not directly related to title optimization, once you create the title of a post, you can also optimize the URL.
An SEO friendly URL is short, descriptive, and includes your target keyword.
For example, if your title is “10 Easy Steps to Setup a New WordPress Blog”, your URL can be “/setup-wordpress-blog”.
Title Tag SEO Examples
Let’s review some examples of well-optimized title tags to understand how keywords can blend into the title nicely creating good titles for both search engines and users.
Example 1: Google Adsense
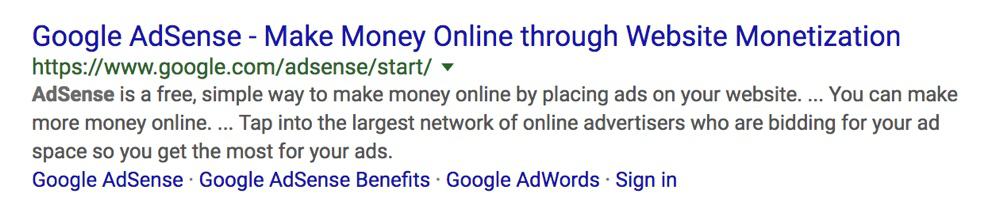
Google Adsense is a known brand so they included their brand name first and then the target keywords “Make money Online”
Example 2: HubSpot

This is a very nice example from HubSpot. Notice how keywords (VR Marketing Examples) are used with power words (Steal)
Example 3: Reliablesoft
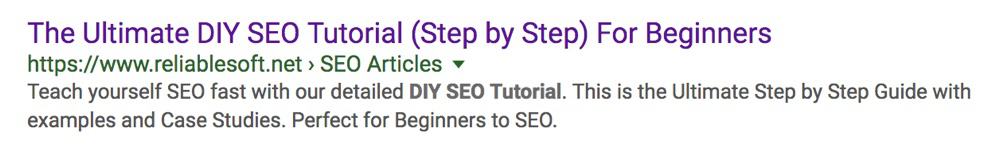
This is an example from one of my posts. It includes power words (Ultimate), keywords (DIY SEO Tutorial), and parenthesis in the title.
Bad Practices
Besides following best practices when writing your page titles, is it equally important to avoid these mistakes.
Avoid making exact match titles based on long-tail keywords
In the past having exact match titles (especially for long tail keywords) was recommended but after the introduction of Rank Brain, this is no longer the case.
What you should do instead is to carry out your keyword research and find out the long-tail keywords to target and then use them as part of your title and not as your title.
Avoid having the same title for a page, as your competitors
Before writing your page title, it’s always a good practice to search Google for your target keywords and analyze the top results.
If you use an exact copy of a page title that is already ranking in Google, then it would be very difficult for you to rank in the top positions.
Google likes to present different titles in the first 10 positions so to increase your chances of appearing in the top 10, you need to differentiate your titles.
To help you understand this better, consider the following example.
Open Google and search for “What is Off Page SEO”. You will something like the screenshot below.
Notice that all titles are unique.
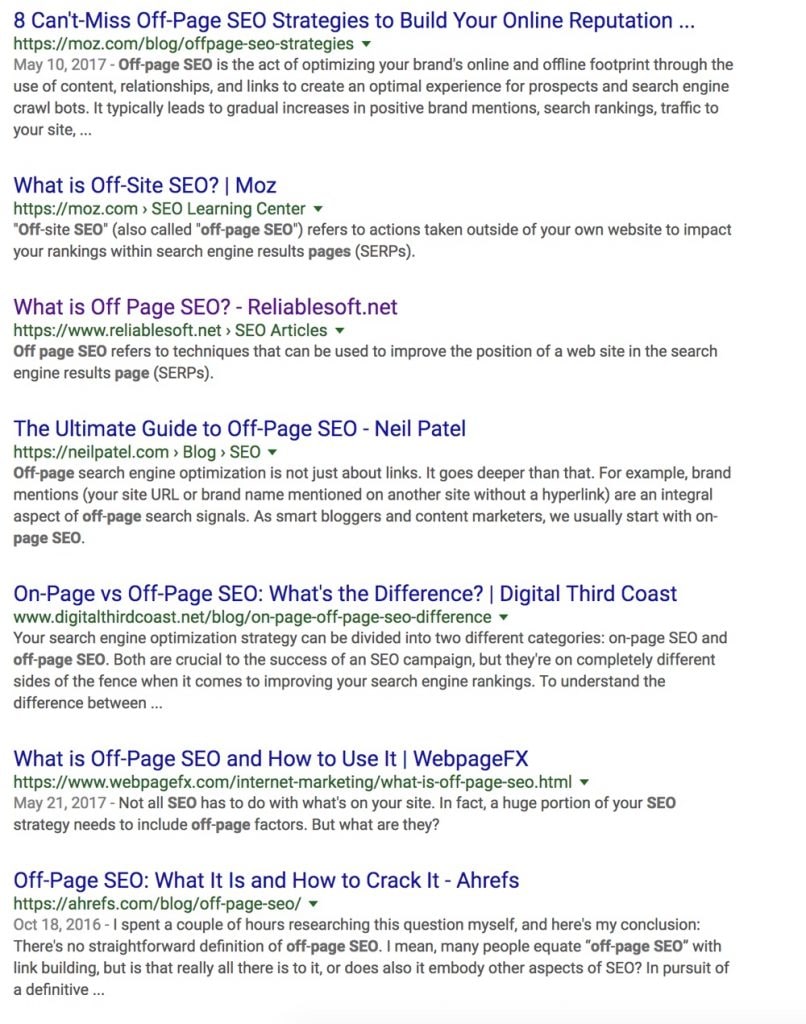
If you were to write a post today about Off-Page SEO, then your title should not be the same as the ones above.
Instead, you could write something different. For example, “Off-Page SEO Made Simple. A Step By Step Guide”.
Optimizing the page title after publication (Must Read)
When you initially publish a post, you create the post title based on the best practices described above, but that’s not the end of the story.
As part of the on-going SEO process, you need to go back and check how your titles are performing and if needed take corrective actions to improve them.
Improving your page titles can potentially increase your CTRs and rankings.
Let me demonstrate how this process works with a real example.
One of the posts published on my nutrition blog (CalorieSecrets.net) had the title: “20 Weight Loss Tips That Actually Work”.
Six months after the post was published, I logged in to SEMRUSH to check how the post was performing in Search.
SEMRUSH can tell you for which keywords and at what position in Google a particular page is ranking, something which is very useful for optimization purposes.
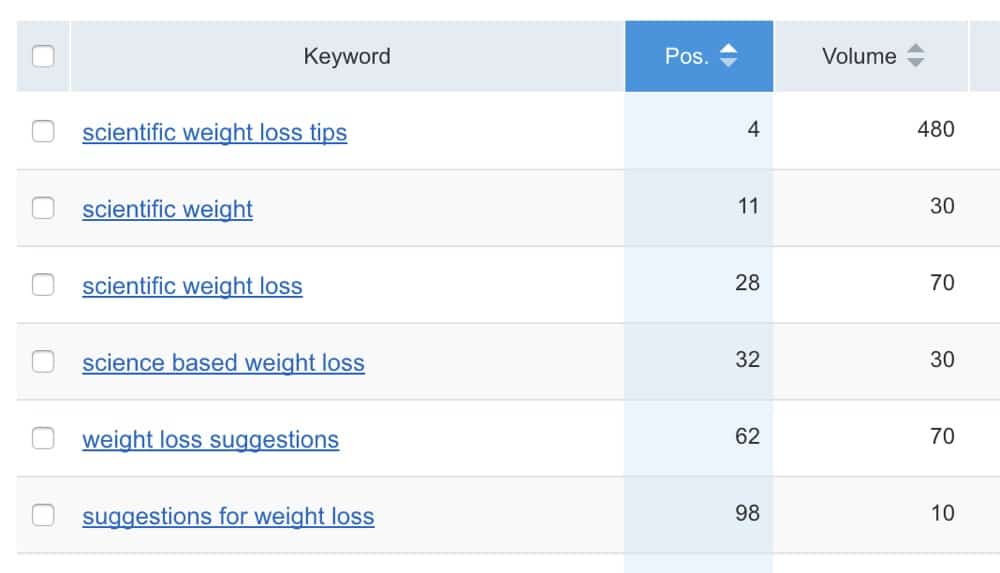
This analysis showed me that the post was ranking for the term “scientific weight loss tips” on page 2 of Google. This was a popular term so I changed my title to include that keyword and I also added power words in parenthesis.
The new title became: “20 Scientific Weight Loss Tips That Actually Work (Evidence Based).

After making the changes I have resubmitted the post to Google using the Fetch and Render function of Google Search Console.
The result? In just 10 days the post was ranking at position 4 of Google for the term “scientific weight loss tips”. That’s a huge improvement in rankings and of course traffic.
How you can take advantage of this?
You can use the exact same procedure to improve the ranking position of your old posts by making changes to your titles.
Unfortunately, you need the paid tools to do this kind of analysis. I like to use SEMRUSH because it offers great features for Digital Marketers but you can use any other tool you want.
Here is a quick overview of the procedure:
- Optimize your titles and publish your posts.
- After 5-6 months go back and check the ranking position of the post for various keywords.
- Change your title to include keywords that are closer to the first page of Google and have a decent amount of monthly search traffic.
- Resubmit the post to Google using the Fetch and Render function of Google Search Console.
- Monitor your rankings.
Conclusion
Page titles are very important for SEO. It is perhaps one of the few SEO elements that were crucial 15 years ago and still gaining importance.
Search engines are looking for the fastest way to understand what topics are covered by a page and the page title serves as a great hint.
On the other hand, users want to find what they want fast, and having titles that stand out will encourage them to click your snippet from the SERPS.
Spend some time thinking about your titles and don’t do them in hurry.
What I do when writing a new blog post is to come up with an initial title (after finishing my keyword research) and then once the post content is finished, I revise the title.
Don’t forget that the best way to find out if your titles are working or need to be improved, is to review your search analytics report (in Google search console) and examine your CTR for a given query.
Increasing the CTR of a post that already has some rankings, will increase traffic and probably it’s ranking position.





it was a wonderful article you wrote, actually users still getting confuse about seo friendly title and meta tags and you shared good article about it. I got a help from this article. thanks for sharing with us.
Thanks a lot Jina, Glad I could help.
Alex
Thank you so much Alex for your help! What you are explaining here is mostly common sense not rocket science like I believed it was. Keep the help coming – I’m eating them up!
Great getting your insights Alex. Disciplining myself to read each one with no disturbances. Thanks.
This is really good information very deep study on the title, people not even think on that much deep but those points very important for ranking and visibility.
Thanks for sharing with us.
My desire is to be a digital marketer in the next six coming months and this article made me more interested to want to study more. Thanks a lot.
This is a really good article for those who want to learn willingly thanks to your information and a platform where I can learn many things about SEO.