Writing for SEO is an art. The job of an SEO writer is to write content for both search engines and users and to do that successfully, you need to know how to apply basic SEO content principles in practice.
In this guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know about SEO writing. I will explain what is SEO writing and the 10 steps to follow to ensure that each content you write is search engine friendly.
You don’t have to be an SEO specialist to write for SEO, but you need to have basic SEO copywriting skills.
Let’s dive in.
What is SEO Writing
SEO writing is the process of writing content that search engines can easily understand. This is done by intelligently adding search phrases or keywords in your content without doing keyword stuffing. SEO writing is also known as SEO copywriting or search engine optimization writing.
How to write for SEO
To become an SEO copywriter, you can follow the 10 steps below.
- Choose your keywords (both head and long tail keywords)
- Craft your page title
- Create an SEO Friendly URL (add your main keyword)
- Write the content (long enough)
- Add your keywords in the first paragraph
- Create headings using long tail keywords
- Add LSI related keywords in your content
- Link to other pages on your website using relevant anchor text
- Demonstrate your Expertise and Authority on the subject (E-A-T)
- Add and Optimize images
Step 1: Choose your keywords (both head and long tail keywords)
The first step before writing new content is to decide which keywords to target.
This process is known as keyword research and its very important for a simple reason. You need to write content around topics that people search for and keyword research will tell you that.
When you do your keyword research, the outcome will be a set of SEO keywords both head (or focus keywords) and long tail keywords that people type in search engines.
The easiest way to do this is to:
- Go to Google and search for your chosen topic (general).
- Visit the top 5 pages and analyze the type of content they provide.
- Take each URL and using SEMRUSH or other tools (ahrefs, ubersuggest, etc) find out for which keywords those pages are ranking and the traffic they get.
- Then depending on the results decide which main keywords you will target in your content.
- Take those keywords again and using a tool, find out the associated long-tail keywords and LSI (or semantic keywords)
Example
Here is an example of how I followed the above steps when writing this post:
I did a general search on Google using “write for SEO”.
I analyzed the first results using SEMRUSH and found out that the keyword that has high volume for my chosen topic is “SEO writing”
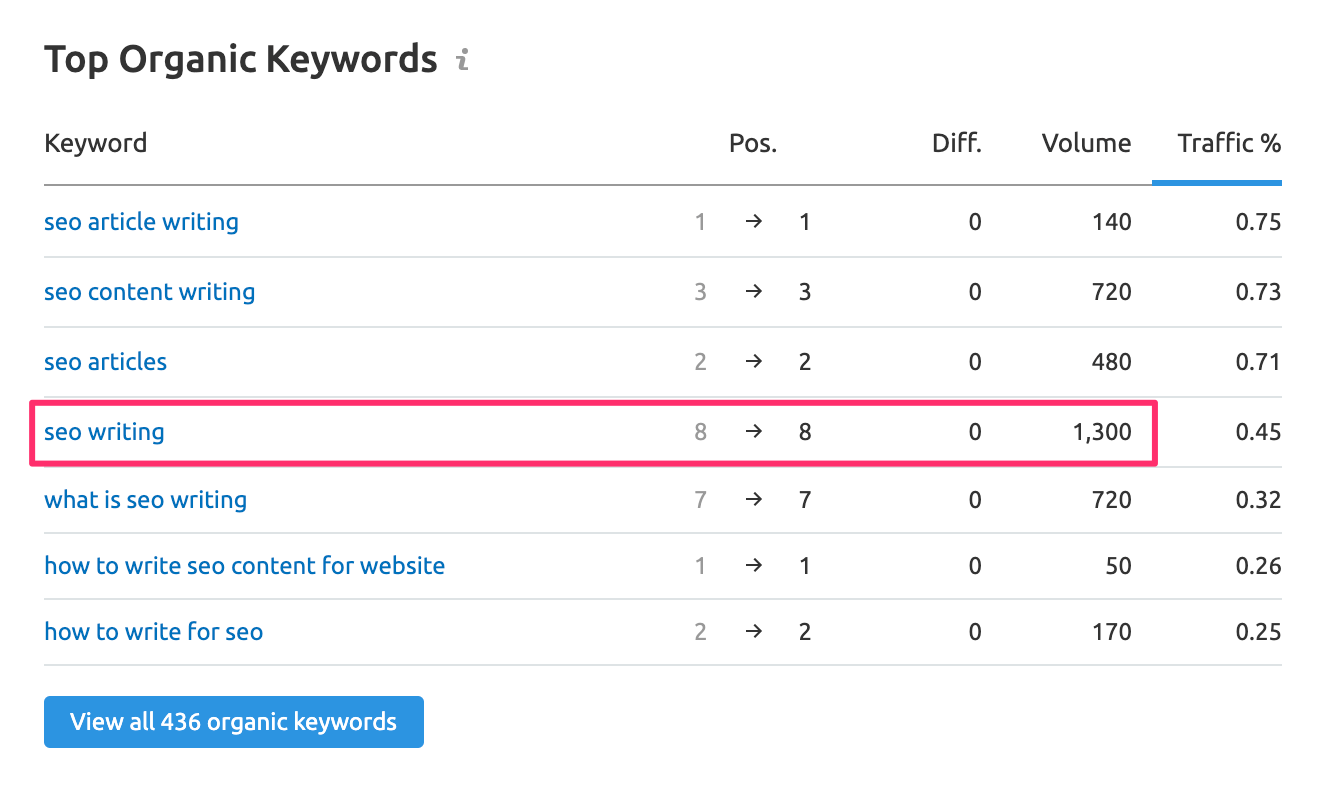
I then used the Keyword Magic tool (utilizing the advanced filters feature) of SEMRUSH to find other related long-tail keywords.
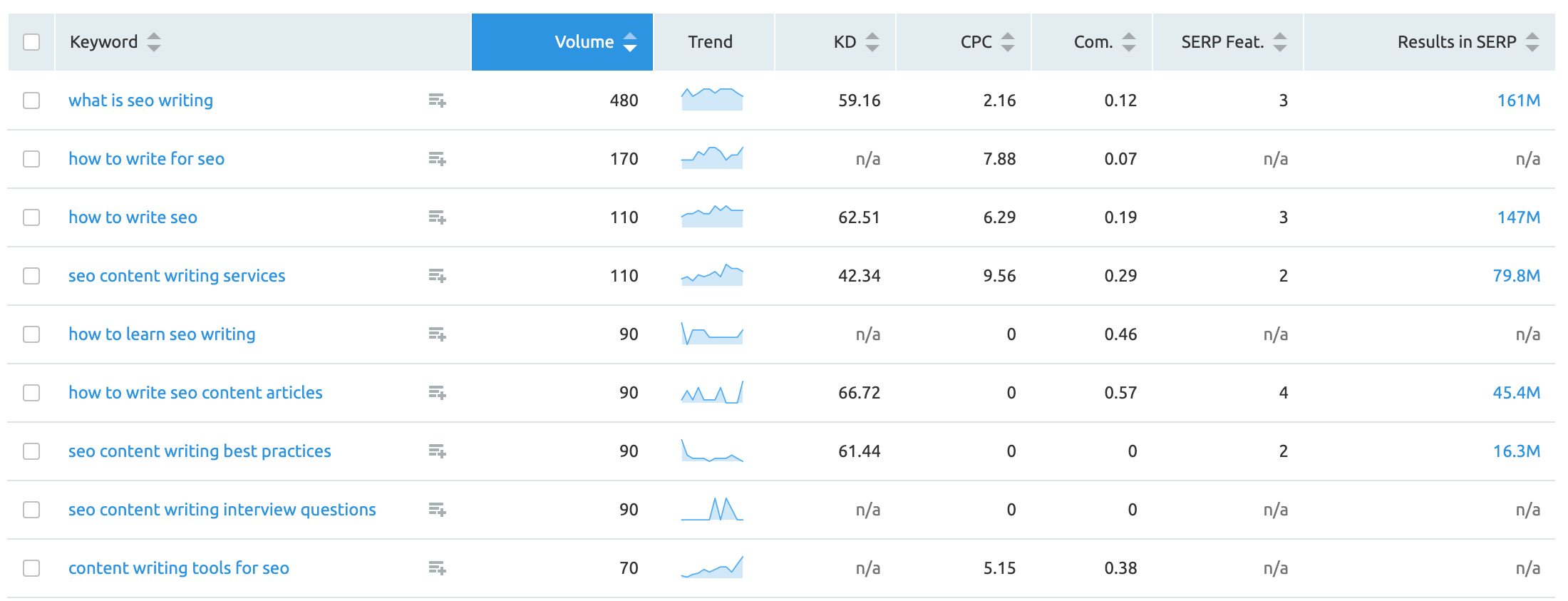
If you take a closer look at the content, you’ll that these keywords are used in different places throughout the article.
By following this process every time you write new content, you help search engines understand your content better and if your content satisfies what users want, this will eventually translate to higher rankings, social media shares and more incoming links.
Step 2: Craft your page title
The next step is to start thinking about your page title. Choosing a good page title is critical for the success of your page or post, so allocate the necessary time to come up with a title that:
- Includes your target keyword
- It’s unique for your website
- It’s interesting for users to click
- It’s around 160 characters
- It’s not the same as the existing titles on the first page of Google.
Don’t omit any of the steps, especially the last one. Before deciding on your title go to Google, type your target keyword and analyze the first 10 titles.
Your goal is to create a title that is unique otherwise you limit your chances of getting a top-10 position since Google rarely shows pages with the same title in the first 10 results.
As an example, look at the title of this post and notice how the main keyword and related are part of my post title.
Recommended Reading: How to create SEO Friendly Titles
Step 3: Create an SEO Friendly URL (add your main keyword)
The next step is very easy to implement. When creating the permalink of your post, make sure that is includes your target keywords and eliminate any unnecessary words.
Look for example at the URL of this post. By default, it was the same as the page title i.e.
https://www.reliablesoft.net/seo-writing-how-to-write-for-seo-10-easy-steps-for-writers/
but I have shortened it down to
https://www.reliablesoft.net/seo-writing
Aim for having exact match URLS where possible.
Recommended Reading: How to create SEO Friendly URLS
Step 4: Write the content (long enough)
Now it’s time to get your hands dirty and get into content writing.
You already know what your competitors have published, you have your title, you know which keywords to include in your content, what else do you need?
What is the user intent?
You need to make sure that you understand the user intent. In other words, your content should match what users want to read for the particular keywords.
One of the ways to find out is to go back to the Google search results and look for patents.
For example, if you are writing an article about ‘SEO tools’, you will notice that almost all results are about lists with ‘Free Tools’.
This means that Google has found out that when users search for tools, although they don’t include the word ‘Free’, their intent is to browse lists of Free tools.
This also means that if you are targeting this keyword, you need to adjust your title and content accordingly, otherwise you minimize your chances of rankings for that term.
How long to make your articles?
Besides the user intent, you also need to make your content comprehensive enough so that users can get accurate and in-depth information about the topic.
Despite what you might have read, there is no magic number when it comes to word length.
It all depends on the topic and keywords. For some topics, you might need to write articles that are over 2000 words, for other topics you can provide a comprehensive answer in 800 words.
Content length alone is NOT a ranking factor. What matters is the quality of the content and how good it can satisfy the real intent of the user.

To avoid any confusion, a number of studies have showed that the ideal article length for SEO is around 1800 words and this is true for many cases.
Longer articles give you the opportunity to use more keywords (without keyword stuffing) and they tend to do better in social media.
But, this is a general guideline and not applicable for all cases. My recommendation is to find the average length of the first 10 results and try to provide a bit more content but better than what is already published.
There is no reason to write a 3000-word article if you can have the same result with a 1500-word article.
Step 5: Add your keywords in the first paragraph
Here is a nice tip that most SEO writers fail to follow. Once you are done with the first draft, you need to go back and revisit your post introduction.
Your goal is to make sure that your target keyword is included in your opening paragraph.
The reason is that Google always considers that content that is above the fold and high on a page is more important than content found down the page.
By adding your keywords in the first paragraph, you give a big clue to Google as to which keywords to associate this page with. It’s also good for the users since you can help them understand that they are on the right page.
Step 6: Create headings using long tail keywords
One of the characteristics of SEO friendly content is that it’s easy to read by both search engines and users, and headings help towards that direction.
Don’t be surprised but the majority of users won’t read your content, they will scan through it. By having meaningful headings, you help them find the part they want faster.
Search engines follow the same pattern, especially for long form content. They scan the page and they look for certain elements to understand how a page is structure and what topics or keywords the content is covering.
To make their job easier you can use predefined heading tags in your HTML like the H1 tag, h2 tag and h3.
Usually a page has only one H1 tag and this is used for the title and then the rest of the content has H2 for the main headings and H3 for the sub-headings.
To further improve the SEO friendliness of your copy, try to use some of your long tail keywords in the headings. Take a closer look at the headings of this article and notice how I have added long-tail keywords in my headings.
Recommended Reading: The complete On-Page SEO Guide
Step 7: Add LSI related keywords in your content
With the introduction of machine learning to Google search algorithms (known as RankBrain), Google is trying to truly understand what the searcher wants by using natural language processing.

This means that for a given keyword, Google will look for the deeper meaning of the query and not just for exact match keywords.
For you as an SEO copywriter it means that you need to add semantically related keywords in your content, to help them during this process.
Semantic keywords are keywords that have the same or similar meaning. You can find these keywords using tools like LSI Graph. Here is a screenshot of the LSI keywords for “SEO writing”.
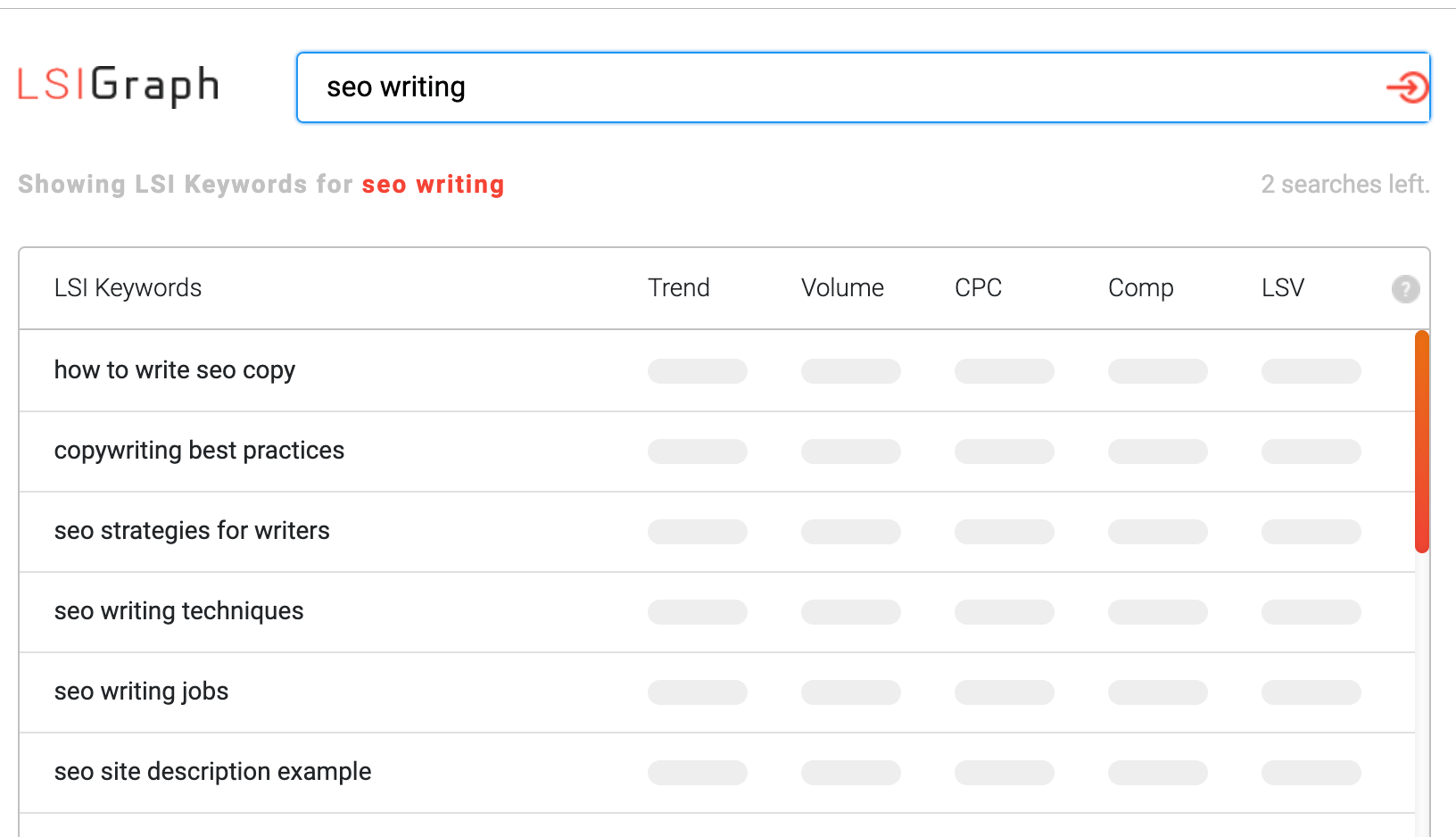
So, you need to go back to your copy and enrich it with LSI keywords in a natural way. You may have to re-phrase some of your sentences but it’s a step that can improve the relevancy of your content.
Step 8: Link to other pages on your website using relevant anchor text
One of the SEO principles most SEO content writers tend to forget is internal linking. An internal link is a link that points to a page on the same website.
Why is it important?
When you publish a new page, it has to match your site’s topics. This improves relevancy and rankings. One of the ways to ‘tell’ Google that your content is relevant with the rest of the site, is to use internal links.
Internal links although they are not as powerful as SEO backlinks, they are still used by Google as a way to understand what the linked page is about, especially if the right anchor text was used in the link.
They also help users learn more about a topic (look at this article again and notice how I have used internal links to give users a way to find out more information about a topic).
Last but not least, internal links are followed by search engine crawlers and this leads to better crawling and indexing of more site pages.
Step 9: Demonstrate your Expertise and Authority on the subject (E-A-T)
There is a lot of content published on the Internet and in order to protect the quality of their search results, Google algorithms can detect which pages demonstrate Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness on a given topic.
In the SEO world this is known as E-A-T and it is a critical factor of SEO content and an indicator of content Quality.
Here is the relevant quote from Google’ guidelines on content quality.

How can you improve your SEO copy for E-A-T?
Follow these simple guidelines:
- Each and every page should have the author name and bio published (see how I’m using this on all my posts).
- A page should have outgoing links to trusted sources
- A page and website in general should have incoming links from other trusted and related websites.
As an SEO copywriter, you cannot control the last guideline (incoming links), since this has to do more with the content promotion part but you can control the first two.
So, revisit your content again and ensure that it links to other trusted websites and that the author bio is clearly shown on all pages.
Step 10: Add and Optimize images
Before you hit the publish button, make sure that your content includes optimized images.
Adding images within your content makes it more interesting and easier to read. While this is not directly related with SEO writing, it can help in a number of ways:
- Users are more likely to share content with high quality images in their social media networks than content with no images.
- You can use the image alt text to give more clues to search engines about your content
- When you properly optimize your images, you have more chances in appearing in Google image search for your target (or related) keywords.
Key Learnings
Anyone can learn to write for SEO. It’s a skill that can be easily mastered through practice and by following some basic SEO principles.
If you are working as a freelancer, there are a lot of SEO writing jobs you can apply for. If you’re doing SEO for your own website, learning how to write content for SEO, will make your content to get found on Google.
The steps to follow are outlined above, what you should not forget is to always put the user first. Your primary concern is to provide content that users want to read and then optimize it for SEO.
This is the reason that I have separated the process into a number of steps that involves writing the content first naturally and then revising it for SEO purposes.
You also can use the same process as a checklist when optimizing content written by non-SEO writers.





hi there,
informative
clear
updated
thanks for the detailed explanation with a presentation, it will be really helpful to enhance in-depth knowledge about Content Writing Skills.
regards,
Wow
Very informative article Alex as usual. Thanks for sharing.