The site structure of an ecommerce website is very important. It has to be easy to navigate, easy to crawl (by search engines) and it’s the starting point to offer a great experience for your users.
A big ecommerce website may have a lot of pages and it’s necessary to have a solid structure so that users can find what they want, in the least possible number of clicks.
Why Ecommerce Site Structure matters?
A good ecommerce site structure has a number of hidden benefits to offer:
Speed: If you have any experience with website speed optimization, you know that when it comes to fine tuning your website’s load speed, you have to deal with a number of things.
Website’s that have a clear structure require less code resources (css, javascript), make fewer requests to the server and they load faster.
In addition, search engine crawlers are able to crawl the website faster, discover more pages and this in turn can have a big impact on your SEO efforts.
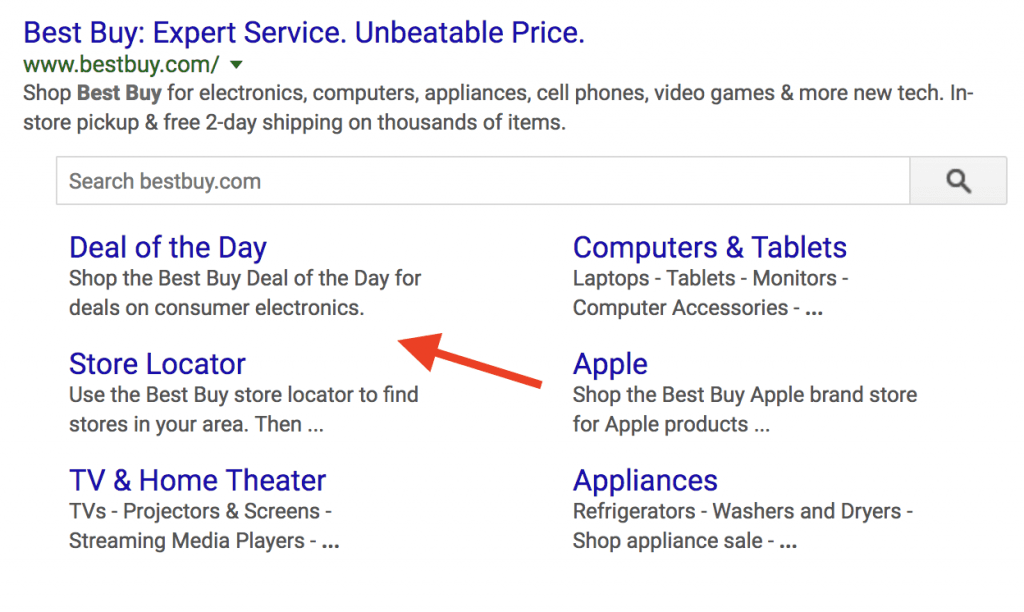
Site links: Site links are shown in the search engine results pages (SERPS), when someone is searching for your company name on Google.
In case of an ecommerce store, sitelinks will show your main categories, like this example from Best Buy.
Sitelinks are great for SEO. Not only they can attract more clicks to the most important pages of your website but they are also good for branding.
The problem is that you cannot specify which pages of your website to include as sitelinks.
It’s up to Google to decide what to show in your snippet. You can use the Google Search Console (site links menu), to exclude pages from showing as sitelinks but not to include.
A poor site structure will minimize your chances of getting sitelinks in the SERPS while a good site structure will help Google pick up the right pages to show as sitelinks along with your title and description.
More conversions: The ultimate goal of every online shop is to generate more sales.
To make sales you have to ‘push’ your potential customers into the sales funnel, which may include a number of other conversions (sign up for newsletter, leads etc).
A well organized and defined site structure is crucial for this process to work as planned.
Visitors should easily find what they want without having to click many times and without spending more time on a page than needed.
6 Steps to Creating the Site Structure for your eCommerce store
Let’s see the steps for creating an SEO optimized structure for your ecommerce shop.
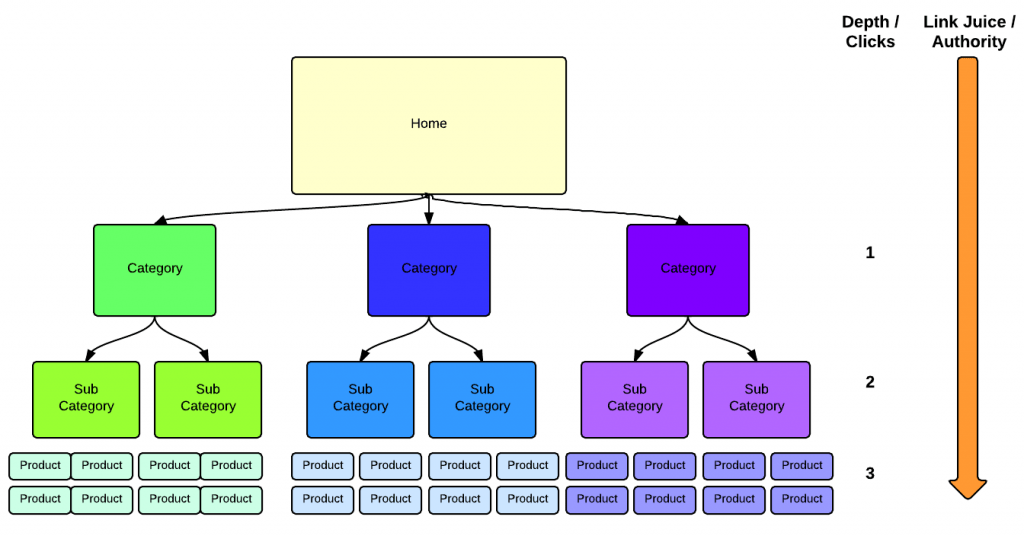
Step 1: Create a Hierarchical structure with no more than 3 levels
An ecommerce website should have a hierarchical structure.
Your home page is at the top of the hierarchy and below you can have 2 or 3 levels before you reach the bottom of the hierarchy – your product pages.
To help you visualize how a hierarchical structure looks like, have a look at the following diagram.
Source: kissmetrics
The home page is at the top of the hierarchy, followed by the main categories (level 1), sub categories (level 2) and finally the product pages (level 3).
The best way to decide on how to create your structure is to take into account the outcome from your keyword research process.
If you haven’t read my previous post on how to do keyword research for an ecommerce website, I suggest you read it before continuing to the next steps.
Keyword research is not only necessary for optimizing your titles and descriptions but it can provide you with ideas on how to structure your website.
Step 2: Create a Simple Menu That Replicates the Site Structure
The navigation i.e. the menus of the shop, should reflect the structure. If you get the structure right, your navigation will be easy to understand and follow.
A few things to take into account, when deciding for your navigation structure and menus:
Keep it simple – When designing the menu structure, always have in mind to keep it as simple as possible.
Avoid adding pages to the menu that are not needed or creating fly out submenus menus when it’s not necessary.
As a rule of thumb, each page on your website should be accessible from the homepage in no more than 3 clicks.
Make use of side menus – When a user selects a particular category from the main menu, you can show them a landing page with a side menu to help them find the products they want.
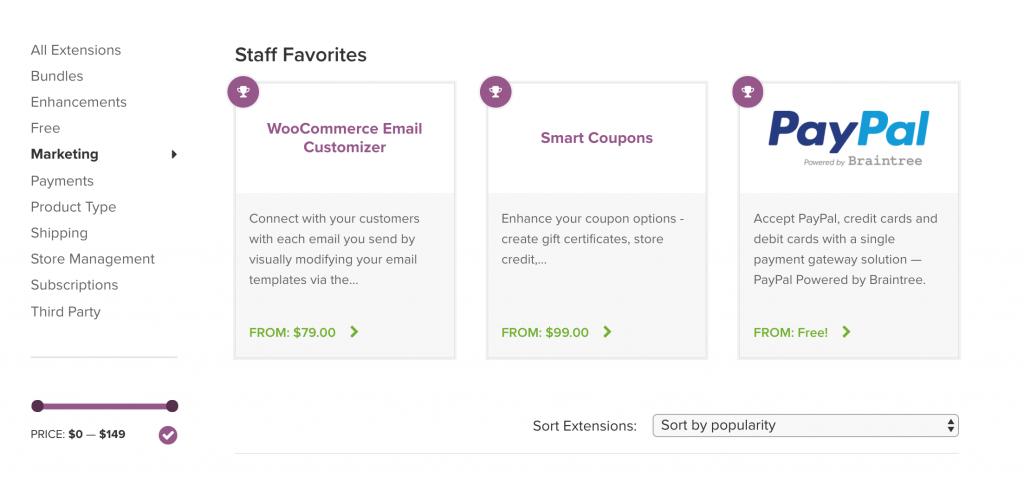
Have a look at how the woocommerce website is structured.
When you choose a category from the main menu, they show you a landing page with all products in that category with several filters (like price) to narrow down your selection.
The other options are also available so that you can choose to change category without having to go back to the menu.
Step 3: Consider creating a separate menu for desktop and mobile
It’s very likely that the majority of your traffic comes from mobile.
This means that you should give special attention on how mobile users navigate your website.
Replicating the desktop menu (as is) it’s not a good option because of the limited screen space available on the mobile device.
What you should do instead is to create a separate menu for mobile and include ONLY those options that are really necessary for navigation purposes.
Pages like privacy policy, about us, etc. can be grouped together thus giving more space on the menu for the important pages (category and product pages).
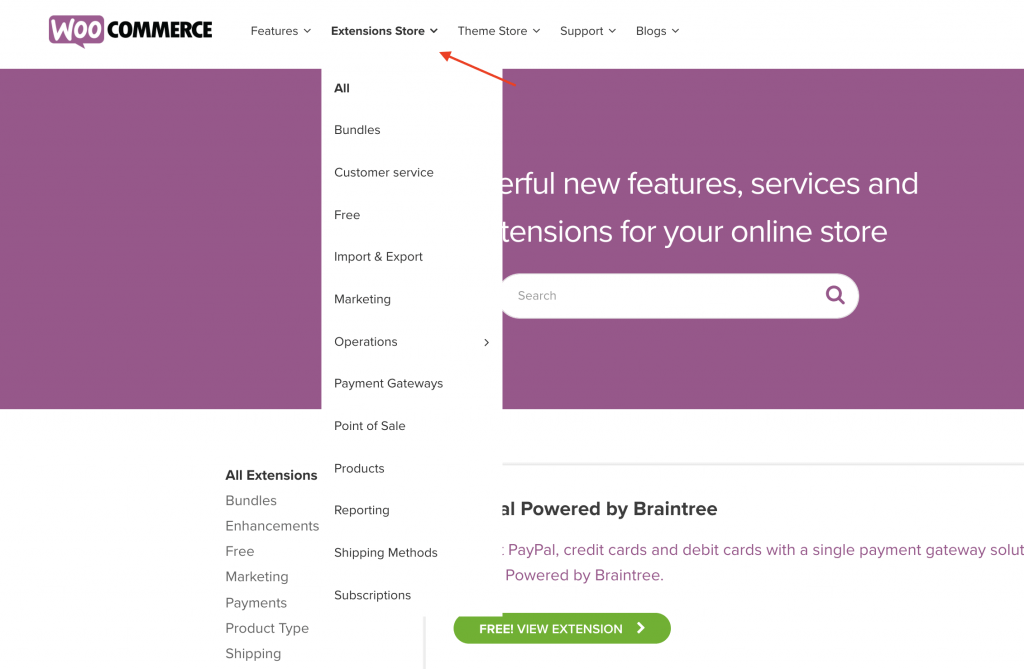
Have a look at woocommerce website again from your desktop and mobile.
On the desktop, they have a full list of products under the Extensions Store menu:
While on mobile they only show the Extensions store option since displaying the full list of products would create a mess and this is not user friendly.
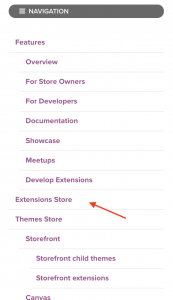
I’m using the same technique on my website, if you check the menu on desktop and mobile, you will notice that the mobile version is simplified.
Step 4: Optimize YOUR URL structure
Having an SEO friendly URL structure helps both users and search engines navigate a website.
The site structure and URL structure are closely related since both have to accurately represent each other.
For example, if you have an ecommerce store selling electronics and have a section for Tablets, then your site structure can be like this:
Home page / Tablets / Android / Ipad
And your URL structure like this:
www.example.com/tablets/android and www.example.com/tablets/ipad
When a word is removed from the URL then the page www.examples/tablets should display all available tablets.
Use the following guidelines to optimize the URL structure of your ecommerce website:
#1 – Keep your URLS as short as possible
#2 – Separate keywords in the URL with “-“ (dashes) and not underscores
#3- Avoid having extra characters that are not needed (for examples numbers that don’t make sense for the user)
#4 – Do include attributes of your products in the URL. For example, if you are selling “black ipads with 64 GB of RAM”, then you can make your product URL to be:
/ipad-64gb-black
In general, include product attributes in the URL that may be used as search keywords.
#5 – Use only lowercase characters and avoid spaces
Make your URLS HTTPS
Having a secure website is very important, especially for ecommerce websites.
Not only it’s an SEO ranking factor, but it’s another way to gain user’s trust.
Read my previous guide, how to migrate your website to https for all the details.
Important: If you decide to change your URL structure, you need to be careful not to lose your SEO and rankings.
The best approach is to use 301 redirects to let users and search engines know that the URL of a page has changed.
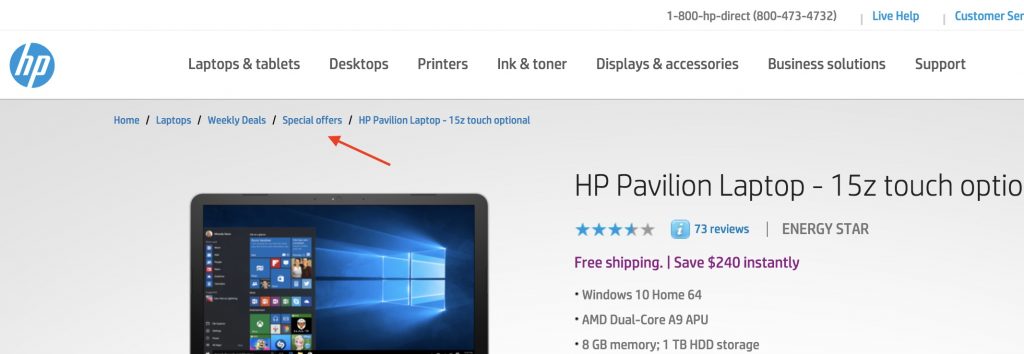
Step 5: Add a breadcrumb menu to all your pages
A breadcrumb menu is shown at the top of a page and it consists of a number of internal links that allows visitors to quickly navigate back to the previous section or the home page of your website.
This is extremely useful when users are searching for a specific product and go back and forth between the categories and products.
It is also useful when users land on a specific product page since they can use the breadcrumb to see what other products are in the same category.
Add structured data to your breadcrumbs
Besides aiding the user navigation while on the site, breadcrumbs are also displayed in the Google search results on mobile and if properly configured can offer an additional advantage for your website in the SERPS.
To make sure that Google can ‘interpret’ breadcrumbs correctly, you need to add the relevant schema.
You can read more details on how to implement schema markup for breadcrumbs here and here.
Step 6: Create a User Sitemap
For all types of websites, it’s always a good practice to create a user-sitemap page.
A user sitemap is different from the XML sitemap that is submitted to search engines.
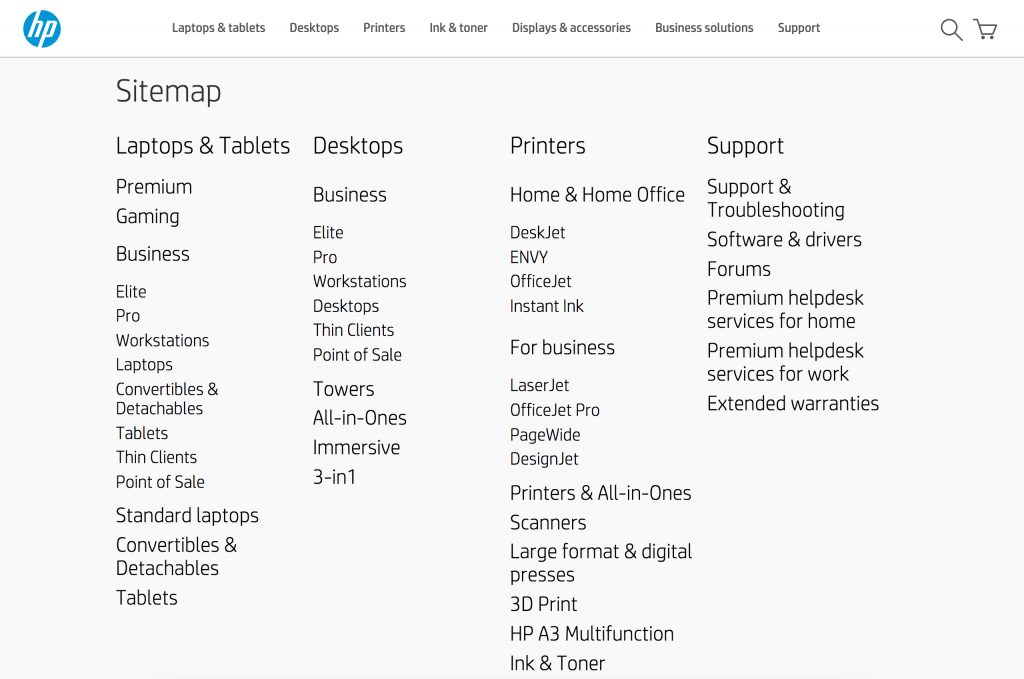
A good user-sitemap page should display all important categories and subcategories of a website is a single page so that users can find easily what they want.
Here is a nice example from HP’s online store.
The User sitemap can be added as an option in the footer.
From experience, when you create the user-sitemap page, it will help you understand if your website is well structured or if you need to make any structural changes to improve it.
Conclusion
Ecommerce websites can quickly grow in size and if you don’t have a solid structure from the beginning, you can easily get lost.
A well-defined structure will help users find what they want fast (in less than 3 clicks), and search engine crawlers will be able to crawl, understand and index your website more efficiently.
When thinking about your shop site structure, consider the following:
- Create a hierarchical site structure
- Your menu should match your site’s hierarchy. Use sidebar menus to aid navigation.
- Give special attention to your mobile version and make sure that the experience of the users’ is optimized for mobile. If necessary, design a separate menu for desktop and mobile.
- Optimize your URLS
- Add a breadcrumb menu to all pages.
- Create a user-sitemap and add it your footer.
Finally, if you already have an ecommerce website with indexed pages and you decide to change the structure and URLS, make use of 301 Redirects so that you don’t lose any of your rankings and domain/page authority.



Being a business owner myself, this blog about eCommerce strategies is quite insightful. It is one of the better sources for procuring ideas to create a better online presence.